Check out our related work:
- iSTFTNet (ICASSP 2022): Fast and lightweight neural vocoder using iSTFT
- iSTFTNet2 (Interspeech 2023): Faster and more lightweight iSTFTNet using 1D-2D CNN
- WaveUNetD (ICASSP 2023): Fast and lightweight discriminator using Wave-U-Net
- AugCondD (ICASSP 2024): Augmentation-conditional discriminator for limited data
Abstract
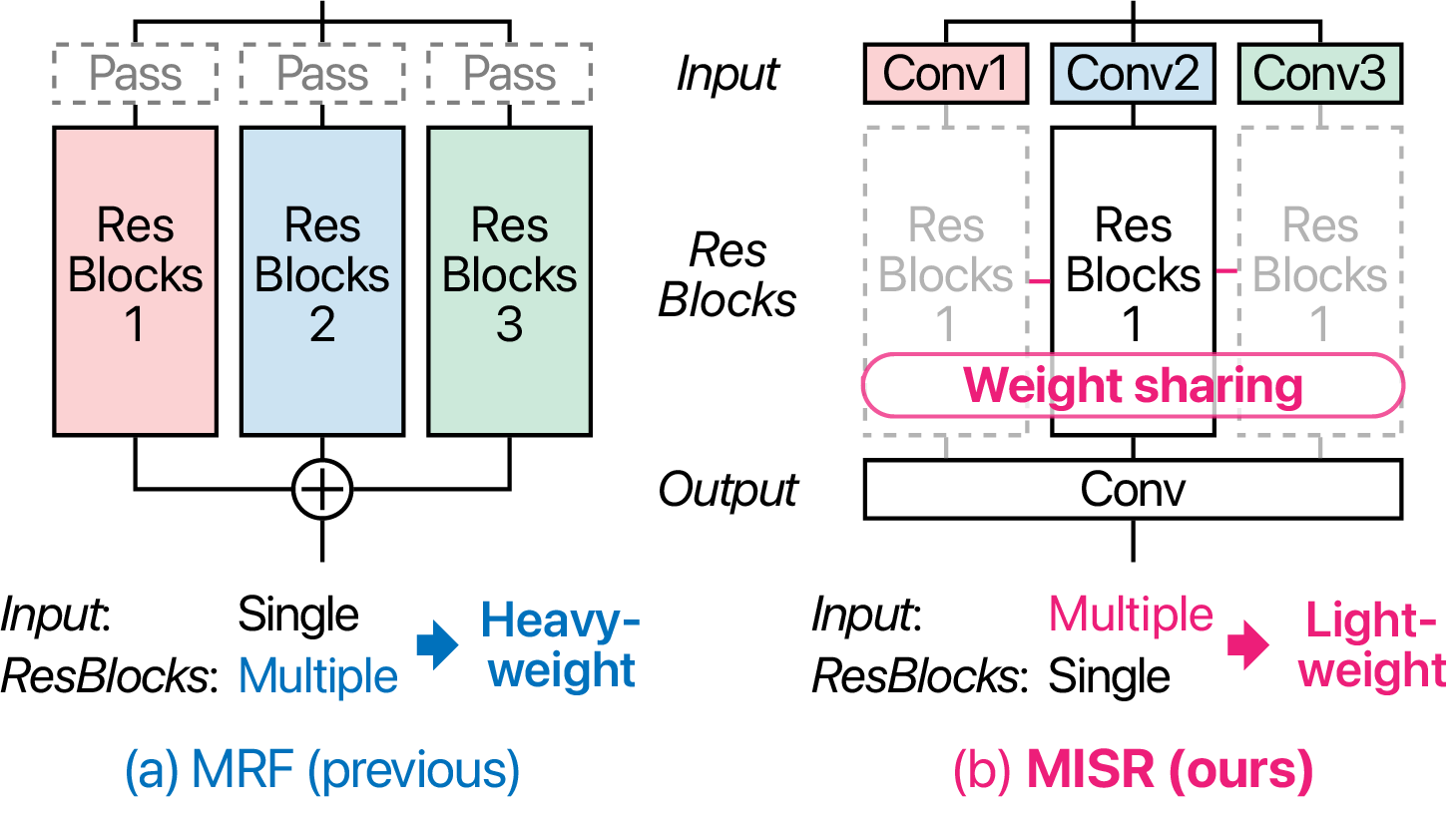
Neural vocoders have recently become popular in text-to-speech synthesis and voice conversion, increasing the demand for efficient neural vocoders. One successful approach is HiFi-GAN, which archives high-fidelity audio synthesis using a relatively small model. This characteristic is obtained using a generator incorporating multi-receptive field fusion (MRF) with multiple branches of residual blocks, allowing the expansion of the description capacity with few-channel convolutions. However, MRF requires the model size to increase with the number of branches. Alternatively, we propose a network called MISRNet, which incorporates a novel module called multi-input single shared residual block (MISR). MISR enlarges the description capacity by enriching the input variation using lightweight convolutions with a kernel size of 1 and, alternatively, reduces the variation of residual blocks from multiple to single. Because the model size of the input convolutions is significantly smaller than that of the residual blocks, MISR reduces the model size compared with that of MRF. Furthermore, we introduce an implementation technique for MISR, where we accelerate the processing speed by adopting tensor reshaping. We experimentally applied our ideas to lightweight variants of HiFi-GAN and iSTFTNet, making the models more lightweight with comparable speech quality and without compromising speed.
Experimental results
I. Main results
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground truth |
| HiFi [1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HiFi-MISR | |||||
| HiFi-SISR | |||||
| HiFi-MISR† | |||||
| HiFi-DSC |
| iSTFT [3] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iSTFT-MISR | |||||
| iSTFT-SISR | |||||
| iSTFT-MISR† | |||||
| iSTFT-DSC |
II. Application to multi-speakers
| Sample 1 (p240) | Sample 2 (p260) | Sample 3 (p280) | Sample 4 (p311) | Sample 5 (p335) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground truth |
| HiFi [1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HiFi-MISR |
| iSTFT [3] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iSTFT-MISR |
III. Application to Japanese
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Sample 4 | Sample 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground truth |
| HiFi [1] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HiFi-MISR |
| iSTFT [3] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iSTFT-MISR |
Citation
@inproceedings{kaneko2022misrnet,
title={{MISRNet}: Lightweight Neural Vocoder Using Multi-Input Single Shared Residual Blocks},
author={Takuhiro Kaneko and Hirokazu Kameoka and Kou Tanaka and Shogo Seki},
booktitle={Interspeech},
year={2022},
}
References
- J. Kong, J. Kim, J. Bae. HiFi-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Efficient and High Fidelity Speech Synthesis. NeurIPS, 2020.
- K. Ito, L. Johnson. The LJ Speech Dataset. 2017.
- T. Kaneko, K. Tanaka, H. Kameoka, S. Seki, iSTFTNet: Fast and Lightweight Mel-Spectrogram Vocoder Incorporating Inverse Short-Time Fourier Transform. ICASSP, 2022.
- J. Yamagishi, C. Veaux, K. MacDonald. CSTR VCTK Corpus: English Multi-speaker Corpus for CSTR Voice Cloning Toolkit. University of Edinburgh. The Centre for Speech Technology Research, 2017.
- R. Sonobe, S. Takamichi, H. Saruwatari. JSUT Corpus: Free Large-Scale Japanese Speech Corpus for End-to-End Speech Synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00354, 2017.